A programming language is a vocabulary and set of grammatical rules for instructing a computer or computing device to perform specific tasks. The term programming language usually refers to high-level languages, such as BASIC , C , C++ , COBOL , Java , FORTRAN , Ada, and Pascal.
Each programming language has a unique set of keywords (words that it understands) and a special syntax for organizing program
instructions.
TYPES OF COMPUTER LANGUAGES:
Machine Code (Machine Languages)
Computer dependent language written in binary is called Machine code or Machine language. Machine code requires a high level programming skill along with sound knowledge of computer architecture and functions. Instructions written in binary are immediately executable without help of any langua translators because computer understands only machine code
ADVANTAGES
1. It is written on machine code so no need to translate it int machine language.
2. It has faster execution than other languages.
3. Other translator type subsidiary programs are not required.
DISADVANTAGES
1. It is difficult to understand and develop a program using machine language.
2. It is machine-oriented language.
3. The knowledge of computer internal architectures is essential for program coding.
4. Time consuming coding.
5. Debugging is tough and difficult.
Machine Code (Machine Languages)
Computer dependent language written in binary is called Machine code or Machine language. Machine code requires a high level programming skill along with sound knowledge of computer architecture and functions. Instructions written in binary are immediately executable without help of any langua translators because computer understands only machine code
ADVANTAGES
1. It is written on machine code so no need to translate it int machine language.
2. It has faster execution than other languages.
3. Other translator type subsidiary programs are not required.
DISADVANTAGES
1. It is difficult to understand and develop a program using machine language.
2. It is machine-oriented language.
3. The knowledge of computer internal architectures is essential for program coding.
4. Time consuming coding.
5. Debugging is tough and difficult.
LOW LEVEL LANGUAGE:
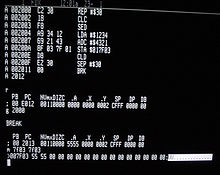
A low-level programming language is a programming language that provides little or no abstraction from a computer's instruction set architecture —commands or functions in the language map closely to processor instructions. Generally this refers to either machine code or assembly language . The word "low" refers to the small or nonexistent amount of abstraction between the language and machine language; because of this, low-level languages are sometimes described as being "close to the hardware". Programs written in low-level languages tend to be relatively non-portable .
Low-level languages can convert to machine code without a compiler or interpreter— second-generation programming languages use a simpler processor called an
assembler — and the resulting code runs directly on the processor. A program written in a low-level language can be made to run very quickly, with a small memory footprint . An equivalent program in a high-level language can be less efficient and use more memory. Low-level languages are simple, but considered difficult to use, due to numerous technical details that the programmer must remember. By comparison, a high-level programming language isolates execution semantics of a computer architecture from the specification of the program, which simplifies development.
Low-level programming languages are sometimes divided into two categories: first generation and second generation ..
ADVANTAGES
1. Coding is faster than machine code language because mnemonics are used for program coding.
2. Less time consumed respect to Machine code languages.
3. Debugging is easy.
DISADVANTAGES
1. Machine oriented language
2. The good knowledge of machine architectures is required.
3. Time consuming
4. Translator is used to translate program into machine code.
5. Not as fast as machine code language in case of execution
Low-level languages can convert to machine code without a compiler or interpreter— second-generation programming languages use a simpler processor called an
assembler — and the resulting code runs directly on the processor. A program written in a low-level language can be made to run very quickly, with a small memory footprint . An equivalent program in a high-level language can be less efficient and use more memory. Low-level languages are simple, but considered difficult to use, due to numerous technical details that the programmer must remember. By comparison, a high-level programming language isolates execution semantics of a computer architecture from the specification of the program, which simplifies development.
Low-level programming languages are sometimes divided into two categories: first generation and second generation ..
ADVANTAGES
1. Coding is faster than machine code language because mnemonics are used for program coding.
2. Less time consumed respect to Machine code languages.
3. Debugging is easy.
DISADVANTAGES
1. Machine oriented language
2. The good knowledge of machine architectures is required.
3. Time consuming
4. Translator is used to translate program into machine code.
5. Not as fast as machine code language in case of execution
HIGH LEVEL LANGUAGE:
"High-level language" refers to the higher level of abstraction from machine language . Rather than dealing with registers, memory addresses and call stacks, high-level languages deal with variables, arrays, objects , complex arithmetic or boolean expressions, subroutines and functions, loops, threads , locks, and other abstract computer science concepts, with a focus on usability over optimal program efficiency. Unlike low-level assembly languages, high-level languages have few, if any, language elements that translate directly into a machine's native opcodes. Other features, such as string handling routines, object-oriented language features, and file input/output, may also be present. One thing to note about high-level programming languages is that these languages allow the programmer to be detached and separated from the machine. That is, unlike low-level languages like assembly or machine language, high-level programming can amplify the programmer's instructions and trigger a lot of data movements in the background without their knowledge. The responsibility and power of executing instructions have been handed over to the machine from the programmer.
ADVANTAGES
1. Simple English is used for program coding.
2. Machine independent
3. Problem and procedure oriented
4. The knowledge of computer architectures is not necessary
5. It requires less time for program coding.
6. Program can be debugged easily
DISADVANTAGES
1. Since it is written in user's language so it should be converted into machine code.So it requires a translator.
2. The execution of the program is slower than machine code
3. The conversion time is slower than assembly language because it is entirely written on human language.
4GL (4th Generation Language)
It is a high level language in which fewer instruction codes ar used to accomplish a particular task. It is non-procedural language. Major 4th generation languages are used to get information from files and databases. These are Database oriented programming language.
Example : DBASE, FOXPRO, SQL, VB Etc
ADVANTAGES
1. Software developed using 4GL are user friendly.
2. It is very easy to develop a program because no need to remember the commands and instructions for the program development and we can use drag and drop type command button to develop the program. These buttons are availabl on the system that helps to develop the program.
DISADVANTAGES
1. Program runs slower because it is heavy in size and design
2. It is required to devote longer time to convert into machin code.
3. Huge sized powerful translators are required to convert
HIGH LEVEL LANGUAGE .V. LOW LEVEL LANGUAGE:
"High-level language" refers to the higher level of abstraction from machine language . Rather than dealing with registers, memory addresses and call stacks, high-level languages deal with variables, arrays, objects , complex arithmetic or boolean expressions, subroutines and functions, loops, threads , locks, and other abstract computer science concepts, with a focus on usability over optimal program efficiency. Unlike low-level assembly languages, high-level languages have few, if any, language elements that translate directly into a machine's native opcodes. Other features, such as string handling routines, object-oriented language features, and file input/output, may also be present. One thing to note about high-level programming languages is that these languages allow the programmer to be detached and separated from the machine. That is, unlike low-level languages like assembly or machine language, high-level programming can amplify the programmer's instructions and trigger a lot of data movements in the background without their knowledge. The responsibility and power of executing instructions have been handed over to the machine from the programmer.
ADVANTAGES
1. Simple English is used for program coding.
2. Machine independent
3. Problem and procedure oriented
4. The knowledge of computer architectures is not necessary
5. It requires less time for program coding.
6. Program can be debugged easily
DISADVANTAGES
1. Since it is written in user's language so it should be converted into machine code.So it requires a translator.
2. The execution of the program is slower than machine code
3. The conversion time is slower than assembly language because it is entirely written on human language.
4GL (4th Generation Language)
It is a high level language in which fewer instruction codes ar used to accomplish a particular task. It is non-procedural language. Major 4th generation languages are used to get information from files and databases. These are Database oriented programming language.
Example : DBASE, FOXPRO, SQL, VB Etc
ADVANTAGES
1. Software developed using 4GL are user friendly.
2. It is very easy to develop a program because no need to remember the commands and instructions for the program development and we can use drag and drop type command button to develop the program. These buttons are availabl on the system that helps to develop the program.
DISADVANTAGES
1. Program runs slower because it is heavy in size and design
2. It is required to devote longer time to convert into machin code.
3. Huge sized powerful translators are required to convert
HIGH LEVEL LANGUAGE .V. LOW LEVEL LANGUAGE:



















No comments:
Post a Comment